- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The role of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin administration on the risk of dementia in bladder cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Previous cohort studies have found an association between Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) administration and incident dementia. In the systematic review and meta-analysis, we aimed to summarize the current evidence of the effect of BCG use on the risk of developing dementia.
Methods
We searched six databases until 20 May 2023 for studies investigating the risk of dementia and BCG administration. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) were pooled in the meta-analysis. Meta-regression, subgroup, and sensitivity analysis were conducted as well.
Results
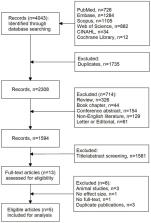
Of the 4,043 records initially evaluated, five articles were included for final analysis, with a total of 45,407 bladder cancer (BC) patients. All five studies were evaluated and rated as with high quality, and a low possibility of publication bias was indicated. A significant association between BCG and the incidence of dementia in BC patients was found in all five studies. Although a high heterogeneity (I 2 = 84.5%, p < 0.001) was observed, the pooled HR was 0.55 (0.42–0.73), indicating that BCG exposure or treatment reduced the risk of incident dementia by 45%. Moreover, the sensitivity analysis showed good robustness of the overall effect with no serious publication bias.
Conclusion
BCG administration is associated with a significantly lower risk of developing dementia. However, an epidemiological cohort is needed to establish a relationship between BCG use and incident dementia in the normal population. Once the relationship is confirmed, more people may benefit from the association.
Related collections
Most cited references42
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found