- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Human Milk Oligosaccharides to Prevent Gut Dysfunction and Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Neonates
Read this article at
Abstract
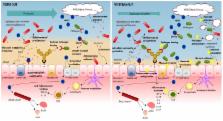
This review focuses on the evidence for health benefits of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) for preterm infants to stimulate gut adaptation and reduce the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in early life. The health benefits of breastfeeding are partly explained by the abundant HMOs that serve as prebiotics and immunomodulators. Gut immaturity in preterm infants leads to difficulties in tolerating enteral feeding and bacterial colonization and a high sensitivity to NEC, particularly when breast milk is insufficient. Due to the immaturity of the preterm infants, their response to HMOs could be different from that in term infants. The concentration of HMOs in human milk is highly variable and there is no evidence to support a specifically adapted high concentration in preterm milk. Further, the gut microbiota is not only different but also highly variable after preterm birth. Studies in pigs as models for preterm infants indicate that HMO supplementation to formula does not mature the gut or prevent NEC during the first weeks after preterm birth and the effects may depend on a certain stage of gut maturity. Supplemented HMOs may become more important for gut protection in the preterm infants when the gut has reached a more mature phase.
Related collections
Most cited references65
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oligosaccharides in human milk: structural, functional, and metabolic aspects.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Necrotising enterocolitis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found