- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 : A Promising Agent for Cardioprotection During Myocardial Ischemia
Read this article at
Summary
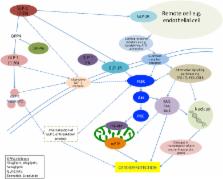
Glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36) amide (GLP-1) is a human incretin hormone responsible for the release of insulin in response to food. Pre-clinical and human physiological studies have demonstrated cardioprotection from ischemia-reperfusion injury. It can reduce infarct size, ischemic left ventricular dysfunction, and myocardial stunning. GLP-1 receptor agonists have also been shown to reduce infarct size in myocardial infarction. The mechanism through which this protection occurs is uncertain but may include hijacking the subcellular pathways of ischemic preconditioning, modulation of myocardial metabolism, and hemodynamic effects including peripheral, pulmonary, and coronary vasodilatation. This review will assess the evidence for each of these mechanisms in turn. Challenges remain in successfully translating cardioprotective interventions from bench-to-bedside. The window of cardioprotection is short and timing of cardioprotection in the appropriate clinical setting is critically important. We will emphasize the need for high-quality, well-designed research to evaluate GLP-1 as a cardioprotective agent for use in real-world practice.
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cardioprotective and vasodilatory actions of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor are mediated through both glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-dependent and -independent pathways.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with acute myocardial infarction and left ventricular dysfunction after successful reperfusion.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mechanisms of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 in the pancreas.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.