- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Impact of Massage Therapy on Function in Pain Populations—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials: Part II, Cancer Pain Populations
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose. Pain is multi-dimensional and may be better addressed through a holistic, biopsychosocial approach. Massage therapy is commonly practiced among patients seeking pain management; however, its efficacy is unclear. This systematic review and meta-analysis is the first to rigorously assess the quality of massage therapy research and evidence for its efficacy in treating pain, function-related and health-related quality of life in cancer populations.
Methods. Key databases were searched from inception through February 2014. Eligible randomized controlled trials were assessed for methodological quality using the SIGN 50 Checklist. Meta-analysis was applied at the outcome level. A diverse steering committee interpreted the results to develop recommendations.
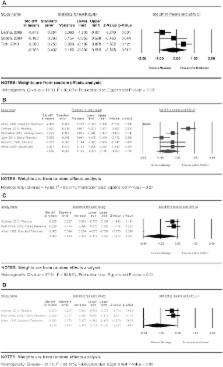
Results. Twelve high quality and four low quality studies were subsequently included in the review. Results demonstrate massage therapy is effective for treating pain compared to no treatment [standardized mean difference (SMD) = −.20] and active (SMD = −0.55) comparators. Compared to active comparators, massage therapy was also found to be beneficial for treating fatigue (SMD = −1.06) and anxiety (SMD = −1.24).
Conclusion. Based on the evidence, weak recommendations are suggested for massage therapy, compared to an active comparator, for the treatment of pain, fatigue, and anxiety. No recommendations were suggested for massage therapy compared to no treatment or sham control based on the available literature to date. This review addresses massage therapy safety, research challenges, how to address identified research gaps, and necessary next steps for implementing massage therapy as a viable pain management option for cancer pain populations.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pain and its treatment in outpatients with metastatic cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found