- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Optimal Self-Tuning PID Controller Based on Low Power Consumption for a Server Fan Cooling System
Read this article at
Abstract
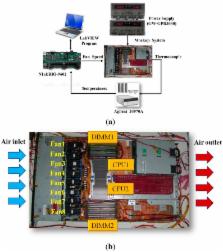
Recently, saving the cooling power in servers by controlling the fan speed has attracted considerable attention because of the increasing demand for high-density servers. This paper presents an optimal self-tuning proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller, combining a PID neural network (PIDNN) with fan-power-based optimization in the transient-state temperature response in the time domain, for a server fan cooling system. Because the thermal model of the cooling system is nonlinear and complex, a server mockup system simulating a 1U rack server was constructed and a fan power model was created using a third-order nonlinear curve fit to determine the cooling power consumption by the fan speed control. PIDNN with a time domain criterion is used to tune all online and optimized PID gains. The proposed controller was validated through experiments of step response when the server operated from the low to high power state. The results show that up to 14% of a server’s fan cooling power can be saved if the fan control permits a slight temperature response overshoot in the electronic components, which may provide a time-saving strategy for tuning the PID controller to control the server fan speed during low fan power consumption.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The future of PID control
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Energy management for commercial servers
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found