- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
IgG4 antibodies and cancer-associated inflammation : Insights into a novel mechanism of immune escape
other
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
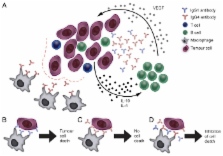
Abstract
The role of B cells and antibodies in cancer is insufficiently understood but is receiving increasing attention. We have recently identified IgG4 as an antibody subclass elicited by melanoma-associated interleukin-10-driven inflammation. In this setting, IgG4 exhibit inefficient immunostimulatory capacity and block the cytotoxic activities of other antibodies. These previously unappreciated mechanisms of immune escape may constitute promising targets for the development of novel anticancer immunotherapies.
Related collections
Most cited references5
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
IgG4 subclass antibodies impair antitumor immunity in melanoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The high-affinity human IgG receptor FcγRI (CD64) promotes IgG-mediated inflammation, anaphylaxis, and antitumor immunotherapy.
Friederike Jönsson, Marc Daëron, Patrick England … (2013)

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Monitoring the Systemic Human Memory B Cell Compartment of Melanoma Patients for Anti-Tumor IgG Antibodies
Amy Gilbert, Panagiotis Karagiannis, Tihomir Dodev … (2011)