- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Association between dietary fiber to carbohydrate ratio and risk of dental caries in diabetic patients: an analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2015–2020
Read this article at
Abstract
Aim
People with diabetes mellitus have a higher risk of dental caries than the general population. Diet is one of the most important factors affecting the risk of dental caries. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of dietary fiber to carbohydrate ratio (FCR) on the risk of dental caries in diabetic patients.
Methods
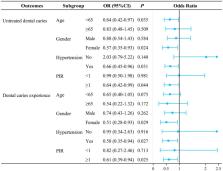
Data of this cross-sectional study were extracted from the 2015–2020 cycle of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database. FCR levels were divided into two categories based on the median (0.13). The outcomes were untreated dental caries and dental caries experience. The associations of FCR with untreated dental caries and dental caries experience were assessed using multivariable logistic regression analysis and reported as odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). Stratified analyses were performed according to age (<65 and ≥ 65 years), gender (female and male), hypertension (yes and no), and the ratio of family income to poverty (PIR, <1 and ≥ 1).
Results
A total of 2,412 patients diagnosed with diabetes were included, of whom 728 (30.18%) had untreated dental caries and 2,104 (87.23%) had dental caries experience. Patients with FCR ≥0.13 were correlated with lower odds of untreated dental caries (OR = 0.72, 95%CI: 0.52–0.99) and dental caries experience (OR = 0.63, 95%CI: 0.42–0.93) compared to patients with FCR <0.13. Stratified analyses demonstrated that patients with FCR ≥0.13 were found to be related to lower odds of untreated dental caries in those aged <65 years (OR = 0.64, 95%CI: 0.42–0.97), female (OR = 0.57, 95%CI: 0.35–0.93), with hypertension (OR = 0.66, 95%CI: 0.45–0.96), and PIR ≥1 (OR = 0.64, 95%CI: 0.42–0.99). Similar results to untreated dental caries were observed in the analysis of dental caries experience ( p < 0.05).
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association's strategic Impact Goal through 2020 and beyond.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found