- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Beyond DNA sensing: expanding the role of cGAS/STING in immunity and diseases
Read this article at
Abstract
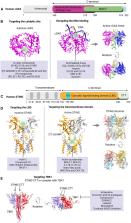
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS) is a DNA sensor that elicits a robust type I interferon response by recognizing ubiquitous danger-associated molecules. The cGAS/stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS/STING) is activated by endogenous DNA, including DNA released from mitochondria and extranuclear chromatin, as well as exogenous DNA derived from pathogenic microorganisms. cGAS/STING is positioned as a key axis of autoimmunity, the inflammatory response, and cancer progression, suggesting that the cGAS/STING signaling pathway represents an efficient therapeutic target. Based on the accumulated evidence, we present insights into the prevention and treatment of cGAS/STING-related chronic immune and inflammatory diseases. This review presents the current state of clinical and nonclinical development of modulators targeting cGAS/STING, providing useful information on the design of therapeutic strategies.
Related collections
Most cited references192
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
STING-dependent cytosolic DNA sensing mediates innate immune recognition of immunogenic tumors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found