- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Synergistic Effect of Hyperthermia and Chemotherapy in Magnetite Nanomedicine-Based Lung Cancer Treatment
Abstract
Background
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer patient death in the world. There are many treatment options for lung cancer, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and combined therapy. Despite significant progress has been made in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer during the past few decades, the prognosis is still unsatisfactory.
Purpose
To resolve the problem of chemotherapy failure, we developed a magnetite-based nanomedicine for chemotherapy acting synergistically with loco-regional hyperthermia.
Methods
The targeting carrier consisted of a complex of superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) and poly(sodium styrene sulfonate) (PSS) at the core and a layer-by-layer shell with cisplatin (CDDP), together with methotrexate – human serum albumin conjugate (MTX−HSA conjugate) for lung cancer-specific targeting, referred to hereafter as SPIO@PSS/CDDP/HSA−MTX nanoparticles (NPs).
Results
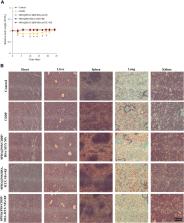
SPIO@PSS/CDDP/HSA−MTX NPs had good biocompatibility and stability in physiological solutions. Furthermore, SPIO@PSS/CDDP/HSA−MTX NPs exhibited a higher temperature increase rate than SPIO nanoparticles under irradiation by a radiofrequency (RF) generator. Therefore, SPIO@PSS/CDDP/HSA−MTX NPs could be used as a hyperthermia inducer under RF exposure after nanoparticles preferentially targeted and then accumulated at tumor sites. In addition, SPIO@PSS/CDDP/HSA−MTX NPs were developed to be used during combined chemotherapy and hyperthermia therapy, exhibiting a synergistic anticancer effect better than the effect of monotherapy.
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found