- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Orexin-1 and orexin-2 receptor antagonists reduce ethanol self-administration in high-drinking rodent models
Read this article at
Abstract
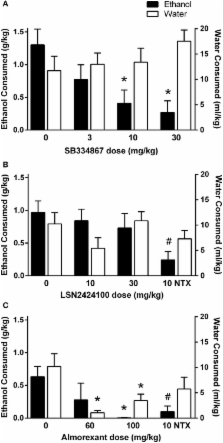
To examine the role of orexin-1 and orexin-2 receptor activity on ethanol self-administration, compounds that differentially target orexin (OX) receptor subtypes were assessed in various self-administration paradigms using high-drinking rodent models. Effects of the OX 1 antagonist SB334867, the OX 2 antagonist LSN2424100, and the mixed OX 1/2 antagonist almorexant (ACT-078573) on home cage ethanol consumption were tested in ethanol-preferring (P) rats using a 2-bottle choice procedure. In separate experiments, effects of SB334867, LSN2424100, and almorexant on operant ethanol self-administration were assessed in P rats maintained on a progressive ratio operant schedule of reinforcement. In a third series of experiments, SB334867, LSN2424100, and almorexant were administered to ethanol-preferring C57BL/6J mice to examine effects of OX receptor blockade on ethanol intake in a binge-like drinking (drinking-in-the-dark) model. In P rats with chronic home cage free-choice ethanol access, SB334867 and almorexant significantly reduced ethanol intake, but almorexant also reduced water intake, suggesting non-specific effects on consummatory behavior. In the progressive ratio operant experiments, LSN2424100 and almorexant reduced breakpoints and ethanol consumption in P rats, whereas the almorexant inactive enantiomer and SB334867 did not significantly affect the motivation to consume ethanol. As expected, vehicle-injected mice exhibited binge-like drinking patterns in the drinking-in-the-dark model. All three OX antagonists reduced both ethanol intake and resulting blood ethanol concentrations relative to vehicle-injected controls, but SB334867 and LSN2424100 also reduced sucrose consumption in a different cohort of mice, suggesting non-specific effects. Collectively, these results contribute to a growing body of evidence indicating that OX 1 and OX 2 receptor activity influences ethanol self-administration, although the effects may not be selective for ethanol consumption.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Progressive ratio schedules in drug self-administration studies in rats: a method to evaluate reinforcing efficacy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found