- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The VTLISFG motif in the BH1 domain plays a significant role in regulating the degradation of Mcl-1 ☆

Read this article at
Abstract
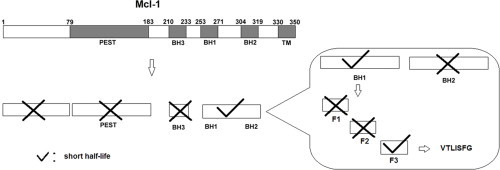
Mcl-1 is a member of the Bcl-2 family protein; its degradation is required for the initiation of apoptosis. The mechanism, however, is not yet clearly known. Previously, it was reported that Mcl-1 is degraded through the ubiquitination-mediated pathway and the PEST domain is the motif responsible for promoting this degradation. We found evidence that this may not be true. We generated several Mcl-1 deletion mutants and examined their effects on protein stability. Deletion of the PEST domain did not prevent the degradation of Mcl-1 during apoptosis. The BH1 domain, but not the PEST, BH3 or BH2 domain, exhibited a short half-life. A peptide named “F3” (VTLISFG) in the C-terminus of the BH1 domain appears to be critical for the rapid turnover of Mcl-1. Deletion of F3 from GFP-Mcl-1-ΔPEST retarded the degradation of this mutant. F3 appeared to be the minimum functional sequence of the degradation motif, since deletion of a single residue was sufficient to abrogate its short half-life. Fusion of F3 with p32 resulted in the degradation of p32 during UV-induced apoptosis, while wild type p32 was not affected. Taken together, these findings suggest that F3 (VTLISFG), instead of PEST, is the major motif responsible for the degradation of Mcl-1 during apoptosis.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
The PEST domain may not be responsible for the short half-life of Mcl-1 during apoptosis.
-
•
A short peptide (F3) inside the BH1 domain was found to have a short half-life.
-
•
Fusion of F3 with p32 impairs the stability of p32 during apoptosis.
-
•
Deletion of F3 increases the stability of GFP-Mcl-1-ΔPEST.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
PEST sequences and regulation by proteolysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found