- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of icaritin in rats by UPLC‐MS/MS

Read this article at
Abstract
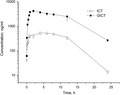
Icaritin (ICT) has distinct bioactivities, especially known for its beneficial effects on bone‐related degenerative disorders; however, its pharmacokinetic properties remain unknown. A novel developed UPLC‐MS/MS method for the determination of ICT and its main metabolite glucuronidated icaritin (GICT) was firstly applied to pharmacokinetic and metabolism studies of ICT in female rats, which were intraperitoneally given 40 mg/kg ICT. Following the protein precipitation of plasma samples with acetonitrile, ICT and GICT were separated on a C18 column using gradient elution mode and quantified in the multiple reaction monitoring mode. The linearities were acceptable for ICT ( r = 0.9960) and GICT ( r = 0.9968), and the lower limit of quantification values was 0.5 and 5 ng/ml, respectively. The accuracy fell in the range of 92.0%–103.1% and precisions were within 9.5%. Good linearity, accuracy, precision, and recovery were achieved for the UPLC‐MS/MS method. ICT was predominantly and rapidly biotransformed to GICT which was slowly eliminated in vivo with a terminal half‐life value of 4.51 hr. Pharmacokinetics of pure ICT eliminated biotransformation interference of Epimedium extract and disclosed genuine pharmacokinetic manner of ICT, as well as firstly elucidated low concentration and bioavailability of ICT in rat plasma.
Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references18

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Icaritin Causes Sustained ERK1/2 Activation and Induces Apoptosis in Human Endometrial Cancer Cells
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Icaritin and its glycosides enhance osteoblastic, but suppress osteoclastic, differentiation and activity in vitro.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found