- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Automatic Planning of Whole Breast Radiation Therapy Using Machine Learning Models
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose: To develop an automatic treatment planning system for whole breast radiation therapy (WBRT) based on two intensity-modulated tangential fields, enabling near-real-time planning.
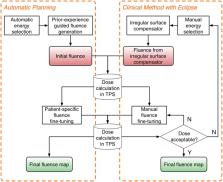
Methods and Materials: A total of 40 WBRT plans from a single institution were included in this study under IRB approval. Twenty WBRT plans, 10 with single energy (SE, 6MV) and 10 with mixed energy (ME, 6/15MV), were randomly selected as training dataset to develop the methodology for automatic planning. The rest 10 SE cases and 10 ME cases served as validation. The auto-planning process consists of three steps. First, an energy prediction model was developed to automate energy selection. This model establishes an anatomy-energy relationship based on principle component analysis (PCA) of the gray level histograms from training cases' digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs). Second, a random forest (RF) model generates an initial fluence map using the selected energies. Third, the balance of overall dose contribution throughout the breast tissue is realized by automatically selecting anchor points and applying centrality correction. The proposed method was tested on the validation dataset. Non-parametric equivalence test was performed for plan quality metrics using one-sided Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test.
Results: For validation, the auto-planning system suggested same energy choices as clinical-plans in 19 out of 20 cases. The mean (standard deviation, SD) of percent target volume covered by 100% prescription dose was 82.5% (4.2%) for auto-plans, and 79.3% (4.8%) for clinical-plans ( p > 0.999). Mean (SD) volume receiving 105% Rx were 95.2 cc (90.7 cc) for auto-plans and 83.9 cc (87.2 cc) for clinical-plans ( p = 0.108). Optimization time for auto-plan was <20 s while clinical manual planning takes between 30 min and 4 h.
Conclusions: We developed an automatic treatment planning system that generates WBRT plans with optimal energy selection, clinically comparable plan quality, and significant reduction in planning time, allowing for near-real-time planning.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Volumetric modulated arc therapy: a review of current literature and clinical use in practice.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Volumetric modulated arc therapy improves dosimetry and reduces treatment time compared to conventional intensity-modulated radiotherapy for locoregional radiotherapy of left-sided breast cancer and internal mammary nodes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found