- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Three-dimensional planning in craniomaxillofacial surgery
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction:
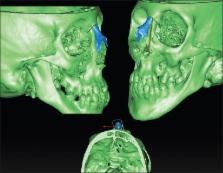
Three-dimensional (3D) planning in oral and maxillofacial surgery has become a standard in the planification of a variety of conditions such as dental implants and orthognathic surgery. By using custom-made cutting and positioning guides, the virtual surgery is exported to the operating room, increasing precision and improving results.
Materials and Methods:
We present our experience in the treatment of craniofacial deformities with 3D planning. Software to plan the different procedures has been selected for each case, depending on the procedure (Nobel Clinician, Kodak 3DS, Simplant O&O, Dolphin 3D, Timeus, Mimics and 3-Matic). The treatment protocol is exposed step by step from virtual planning, design, and printing of the cutting and positioning guides to patients’ outcomes.
Conclusions:
3D planning reduces the surgical time and allows predicting possible difficulties and complications. On the other hand, it increases preoperative planning time and needs a learning curve. The only drawback is the cost of the procedure. At present, the additional preoperative work can be justified because of surgical time reduction and more predictable results. In the future, the cost and time investment will be reduced. 3D planning is here to stay. It is already a fact in craniofacial surgery and the investment is completely justified by the risk reduction and precise results.
Related collections
Most cited references12
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Three-dimensional treatment planning of orthognathic surgery in the era of virtual imaging.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
3D planning in orthognathic surgery: CAD/CAM surgical splints and prediction of the soft and hard tissues results - our experience in 16 cases.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found