- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T variant and hyperhomocysteinemia in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients from India
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Related collections
Most cited references49
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Purification of nucleic acids by extraction with phenol:chloroform.
Joseph F Sambrook, David Russell (2006)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
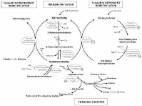
The Molecular and Cellular Effect of Homocysteine Metabolism Imbalance on Human Health
Henrieta Skovierová, Eva Vidomanová, Silvia Mahmood … (2016)
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Geographical and ethnic variation of the 677C>T allele of 5,10 methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR): findings from over 7000 newborns from 16 areas world wide.
B Wilcken, Robert Hofstra (2003)