- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Early long-term administration of the CSF1R inhibitor PLX3397 ablates microglia and reduces accumulation of intraneuronal amyloid, neuritic plaque deposition and pre-fibrillar oligomers in 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
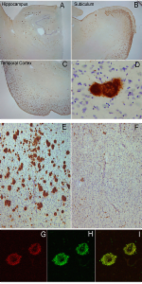
Besides the two main classical features of amyloid beta aggregation and tau-containing neurofibrillary tangle deposition, neuroinflammation plays an important yet unclear role in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Microglia are believed to be key mediators of neuroinflammation during AD and responsible for the regulation of brain homeostasis by balancing neurotoxicity and neuroprotective events. We have previously reported evidence that neuritic plaques are derived from dead neurons that have accumulated intraneuronal amyloid and further recruit Iba1-positive cells, which play a role in either neuronal demise or neuritic plaque maturation or both.
Methods
To study the impact of microglia on neuritic plaque development, we treated two-month-old 5XFAD mice with a selective colony stimulation factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) inhibitor, PLX3397, for a period of 3 months, resulting in a significant ablation of microglia. Directly after this treatment, we analyzed the amount of intraneuronal amyloid and neuritic plaques and performed behavioral studies including Y-maze, fear conditioning and elevated plus maze.
Results
We found that early long-term PLX3397 administration results in a dramatic reduction of both intraneuronal amyloid as well as neuritic plaque deposition. PLX3397 treated young 5XFAD mice also displayed a significant decrease of soluble fibrillar amyloid oligomers in brain lysates, a depletion of soluble pre-fibrillar oligomers in plasma and an improvement in cognitive function measured by fear conditioning tests.
Conclusions
Our findings demonstrate that CSF1R signaling, either directly on neurons or mediated by microglia, is crucial for the accumulation of intraneuronal amyloid and formation of neuritic plaques, suggesting that these two events are serially linked in a causal pathway leading to neurodegeneration and neuritic plaque formation. CSF1R inhibitors represent potential preventative or therapeutic approach that target the very earliest stages of the formation of intraneuronal amyloid and neuritic plaques.
Related collections
Most cited references22
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Common structure of soluble amyloid oligomers implies common mechanism of pathogenesis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Fibril specific, conformation dependent antibodies recognize a generic epitope common to amyloid fibrils and fibrillar oligomers that is absent in prefibrillar oligomers

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found