- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Acetaminophen administration in pediatric age: an observational prospective cross-sectional study

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Parents often do not consider fever as an important physiological response and mechanism of defense against infections that leads to inappropriate use of antipyretics and potentially dangerous side effects. This study is designed to evaluate the appropriateness of antipyretics dosages generally administered to children with fever, and to identify factors that may influence dosage accuracy.
Results
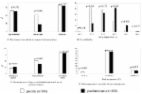
In this cross-sectional study we analyzed the clinical records of 1397 children aged >1 month and < 16 years, requiring a primary care (ambulatory) outpatient visit due to fever. We evaluated the number of children who had received >90 mg/kg/day of acetaminophen, the prescriber, the medication formula and the educational level of the caregiver who administered acetaminophen. Among those children included in our study, 74 % were administered acetaminophen for body temperature ≤ 38.4 °C. 24.12 % of children received >90 mg/kg/day of acetaminophen. Parents with university qualifications most commonly self-administered acetaminophen to their children, in a higher than standard dose. Self medication was also described in 60 % of children, whose acetaminophen was administered for temperatures < 38 °C. Acetaminophen over-dosage was also favored by the use of drug formulations as drops or syrup.
Conclusions
Our study shows that preventive action should be taken regarding the use of acetaminophen as antipyretic drug in children in order to reduce the fever phobia and self-prescription, especially of caregivers with higher educational levels. It is also necessary to promote a more appropriate use of acetaminophen in those parents using drops or syrup formulations.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fever and antipyretic use in children.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Self-medication in university students from the city of Rio Grande, Brazil
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found