- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Expression of Tspan8 in Patients with Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Its Relationship with Clinicopathological Features and Prognosis
Read this article at
Abstract
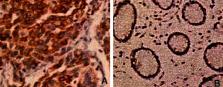
The incidence and mortality of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) are increasing worldwide. High invasion and metastasis are one of the main causes of death in patients. The selection of reasonable and effective molecular markers to evaluate the prognosis of patients with ICC has important clinical guiding significance. In this study, the expression of Tspan protein in ICC and normal tissues was compared, the correlation between Tspan expression and pathological features of patients was analyzed by the logistic regression model using multivariate analysis, and the relationship between Tspan8 expression and prognosis of ICC patients was analyzed by the Kaplan–Meier survival curve. The results showed that Tspan8 is highly positive in ICC tissues, TNM stage, degree of tumor differentiation, lymph node metastasis, and Tspan8 protein expression were independently correlated, and the overexpression of Tspan was associated with the prognosis of ICC invasion and metastasis. This provides a new idea for clinical treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Systemic therapies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: the AJCC/UICC 8th edition updates

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found