- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
1,3-propanediol production with Citrobacter werkmanii DSM17579: effect of a dhaD knock-out
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
1,3-propanediol (PDO) is a substantially industrial metabolite used in the polymer industry. Although several natural PDO production hosts exist, e.g. Klebsiella sp., Citrobacter sp. and Clostridium sp., the PDO yield on glycerol is insufficient for an economically viable bio-process. Enhancing this yield via strain improvement can be achieved by disconnecting the production and growth pathways. In the case of PDO formation, this approach results in a microorganism metabolizing glycerol strictly for PDO production, while catabolizing a co-substrate for growth and maintenance. We applied this strategy to improve the PDO production with Citrobacter werkmanii DSM17579 .
Results
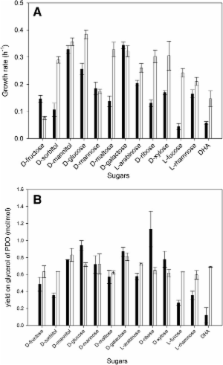
Genetic tools were developed and used to create Citrobacter werkmanii DSM17579 ∆ dhaD in which dhaD, encoding for glycerol dehydrogenase, was deleted. Since this strain was unable to grow on glycerol anaerobically, both pathways were disconnected. The knock-out strain was perturbed with 13 different co-substrates for growth and maintenance. Glucose was the most promising, although a competition between NADH-consuming enzymes and 1,3-propanediol dehydrogenase emerged.
Conclusion
Due to the deletion of dhaD in Citrobacter werkmanii DSM17579, the PDO production and growth pathway were split. As a consequence, the PDO yield on glycerol was improved 1,5 times, strengthening the idea that Citrobacter werkmanii DSM17579 could become an industrially interesting host for PDO production.
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A rapid and simple method for inactivating chromosomal genes in Yersinia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Eliminating side products and increasing succinate yields in engineered strains of Escherichia coli C.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found