- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Resetting the agenda for antibiotic resistance through a health systems perspective
Read this article at
Abstract
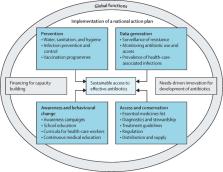
Although the individual and societal consequences of antibiotic resistance spiral upwards, coordinated action has not kept pace on a global scale. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for resilient health systems and has resulted in an unprecedented rate of collaboration in scientific, medical, social, and political dimensions. The pandemic has also created a renewed awareness of the importance of infectious diseases and is a substantial entry point for reigniting the momentum towards containing the silent pandemic of antibiotic resistance. In this Viewpoint, we discuss the limitations in the current narrative on antibiotic resistance and how it could be improved, including concerted efforts to close essential data gaps. We discuss the need for capacity building and coordination at the national and global levels to strengthen the understanding of the importance of sustainable access to effective antibiotics for all health systems that could generate tangible links to current processes for global health and development.
Related collections
Most cited references27

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Will 10 Million People Die a Year due to Antimicrobial Resistance by 2050?

