- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Monitoring of land use land cover dynamics and prediction of urban growth using Land Change Modeler in Delhi and its environs, India
Abstract
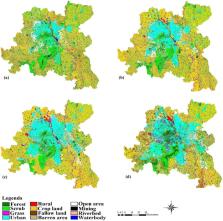
In the recent decades, cities have been expanding at a great pace which changes the landscape rapidly as a result of inflow of people from rural areas and economic progression. Therefore, understanding spatiotemporal dynamics of human induced land use land cover changes has become an important issue to deal with the challenges for making sustainable cities. This study aims to determine the rate of landscape transformations along with its causes and consequences as well as predicting urban growth pattern in Delhi and its environs. Landsat satellite images of 1989, 2000, 2010 and 2020 were used to determine the changes in land use land cover using supervised maximum likelihood classification. Subsequently, Land Change Modeler (LCM) module of TerrSet software was used to generate future urban growth for the year 2030 based on 2010 and 2020 dataset. Validation was carried out by overlaying the actual and simulated 2020 maps. The change detection results showed that urban and open areas increased by 13.44% and 2.40%, respectively, with a substantial decrease in crop land (10.88%) from 1989 to 2020 and forest area increased by 3.48% in 2020 due to restoration programmes. Furthermore, the simulated output of 2030 predicted an increase of 24.30% in urban area and kappa coefficient 0.96. Thus, knowledge of the present and predicted changes will help decision-makers and planners during the process of formulating new sustainable policies, master plans and economic strategies for rapidly growing cities with urban blue-green infrastructures.
Related collections
Most cited references63
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Review Article Digital change detection techniques using remotely-sensed data
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Integration of logistic regression, Markov chain and cellular automata models to simulate urban expansion
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.