- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Nutritional geometry and fitness consequences in Drosophila suzukii, the Spotted‐Wing Drosophila
Read this article at
Abstract
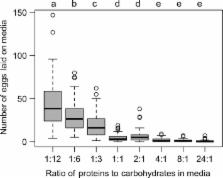
Since its arrival to North America less than a decade ago, the invasive Spotted‐Wing Drosophila ( Drosophila suzukii) has inflicted substantial economic losses on soft fruit agriculture due to its ability to oviposit into ripening fruits. More effective management approaches for this species are needed, but little is known about the factors that influence behavioral choices made by D. suzukii when selecting hosts, or the consequences that their offspring experience when developing in different environments. Using a nutritional geometry methodology, we found that the ratio of proteins‐to‐carbohydrates (P:C) present in media greatly influenced adult D. suzukii behavior and subsequent offspring development. Whereas adult flies showed a strong bias in their oviposition and association behaviors toward carbohydrate‐rich foods, larval survival and eclosion rate were strongly dependent on protein availability. Here, we explore the preference–performance hypothesis (PPH), in which females are predicted to oviposit on medias that provide the greatest offspring benefits, in regard to its relevance in D. suzukii behavior and consequences for management. Our results provide valuable insight into the ecology and evolution of this species that may hopefully lead to more effective management strategies.
Related collections
Most cited references48
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A meta-analysis of preference-performance relationships in phytophagous insects.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gut-associated microbes of Drosophila melanogaster.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found