- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Monitoring of Hypercoagulability by Thromboelastography in Bariatric Surgery
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Obesity is known as a major risk factor for postoperative vein thrombosis. Thromboelastography (TEG) is used to monitor viscoelastic features of blood clots. The aim of this study was to determine hypercoagulable states in patients undergoing bariatric surgery and to assess dynamics of coagulation parameters in the perioperative setting using TEG.
Material/Methods
We included 60 consecutive patients undergoing bariatric surgery. TEG alterations were assessed at 4 time points: at baseline, after the surgery, and on postoperative day 1 (POD1) and 2 (POD2). Hypercoagulable state was defined when patients showed clot strength (G) of ≥11 dynes/cm 2 or maximum amplitude (MA) ≥68 mm.
Results
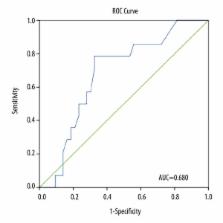
Fourteen patients (23.3%) out of 60 showed hypercoagulability prior to surgery on TEG. Fibrinogen levels were significantly higher in the G ≥11 group compared to the G <11 group, at 4.2 and 3.8 g/l, respectively (p=0.02). Seventeen patients (28.3%) had MA ≥68 mm at baseline. Fibrinogen levels increased significantly from 3.90 at baseline to 4.16 g/l in POD2 (p<0.001). There was an increase in mean reaction time from baseline (6.74 s) to POD2 (7.43 s, p=0.022). We found a correlation between baseline fibrinogen levels and MA (R=0.431, p=0.001) or G (R=0.387, p=0.003). ROC curve analysis showed that fibrinogen levels can predict clot strength (G) ≥11 dynes/cm 2 with AUC=0.680 (p=0.044).
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
TEG and ROTEM: technology and clinical applications.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Management of obesity: improvement of health-care training and systems for prevention and care.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found