- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
New Carbapenemase Inhibitors: Clearing the Way for the β-Lactams
Read this article at
Abstract
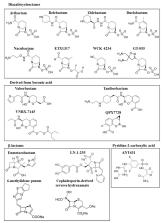
Carbapenem resistance is a major global health problem that seriously compromises the treatment of infections caused by nosocomial pathogens. Resistance to carbapenems mainly occurs via the production of carbapenemases, such as VIM, IMP, NDM, KPC and OXA, among others. Preclinical and clinical trials are currently underway to test a new generation of promising inhibitors, together with the recently approved avibactam, relebactam and vaborbactam. This review summarizes the main, most promising carbapenemase inhibitors synthesized to date, as well as their spectrum of activity and current stage of development. We particularly focus on β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations that could potentially be used to treat infections caused by carbapenemase-producer pathogens of critical priority. The emergence of these new combinations represents a step forward in the fight against antimicrobial resistance, especially in regard to metallo-β-lactamases and carbapenem-hydrolysing class D β-lactamases, not currently inhibited by any clinically approved inhibitor.
Related collections
Most cited references172
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Carbapenemases: the versatile beta-lactamases.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found