- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Health Benefits of Nut Consumption
Read this article at
Abstract
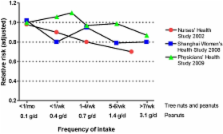
Nuts (tree nuts and peanuts) are nutrient dense foods with complex matrices rich in unsaturated fatty and other bioactive compounds: high-quality vegetable protein, fiber, minerals, tocopherols, phytosterols, and phenolic compounds. By virtue of their unique composition, nuts are likely to beneficially impact health outcomes. Epidemiologic studies have associated nut consumption with a reduced incidence of coronary heart disease and gallstones in both genders and diabetes in women. Limited evidence also suggests beneficial effects on hypertension, cancer, and inflammation. Interventional studies consistently show that nut intake has a cholesterol-lowering effect, even in the context of healthy diets, and there is emerging evidence of beneficial effects on oxidative stress, inflammation, and vascular reactivity. Blood pressure, visceral adiposity and the metabolic syndrome also appear to be positively influenced by nut consumption. Thus it is clear that nuts have a beneficial impact on many cardiovascular risk factors. Contrary to expectations, epidemiologic studies and clinical trials suggest that regular nut consumption is unlikely to contribute to obesity and may even help in weight loss. Safety concerns are limited to the infrequent occurrence of nut allergy in children. In conclusion, nuts are nutrient rich foods with wide-ranging cardiovascular and metabolic benefits, which can be readily incorporated into healthy diets.
Related collections
Most cited references141
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Paleolithic nutrition. A consideration of its nature and current implications.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Regulation of inflammation and redox signaling by dietary polyphenols.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found