- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A human functional protein interaction network and its application to cancer data analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
A high-quality human functional protein interaction network is constructed. Its utility is demonstrated in the identification of cancer candidate genes.
Abstract
Background
One challenge facing biologists is to tease out useful information from massive data sets for further analysis. A pathway-based analysis may shed light by projecting candidate genes onto protein functional relationship networks. We are building such a pathway-based analysis system.
Results
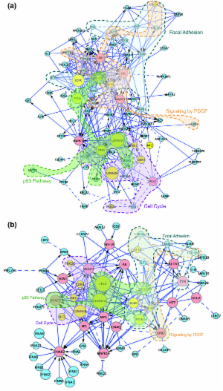
We have constructed a protein functional interaction network by extending curated pathways with non-curated sources of information, including protein-protein interactions, gene coexpression, protein domain interaction, Gene Ontology (GO) annotations and text-mined protein interactions, which cover close to 50% of the human proteome. By applying this network to two glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) data sets and projecting cancer candidate genes onto the network, we found that the majority of GBM candidate genes form a cluster and are closer than expected by chance, and the majority of GBM samples have sequence-altered genes in two network modules, one mainly comprising genes whose products are localized in the cytoplasm and plasma membrane, and another comprising gene products in the nucleus. Both modules are highly enriched in known oncogenes, tumor suppressors and genes involved in signal transduction. Similar network patterns were also found in breast, colorectal and pancreatic cancers.
Conclusions
We have built a highly reliable functional interaction network upon expert-curated pathways and applied this network to the analysis of two genome-wide GBM and several other cancer data sets. The network patterns revealed from our results suggest common mechanisms in the cancer biology. Our system should provide a foundation for a network or pathway-based analysis platform for cancer and other diseases.
Related collections
Most cited references66
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Emergence of scaling in random networks
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found