- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Platelet Count to Spleen Diameter Ratio for the Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Varices in Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
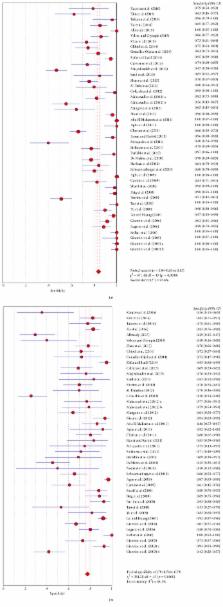
Platelet count to spleen diameter ratio (PSR) was studied extensively as a noninvasive method of diagnosis for varices. The present study aimed to systematically assess the performance of PSR in the diagnosis of varices. PubMed, EMBASE, and article references were searched. The summary receiver operating characteristic curves (AUSROCs), sensitivities, specificities, positive and negative likelihood ratio, and diagnostic odds ratio were calculated. The heterogeneity, quality, and publication bias of studies were evaluated. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses were performed. A total of 49 papers were included. The AUSROCs of PSR for any varices and high-risk varices were 0.8719 and 0.8132, respectively. The summary sensitivities of PSR for any varices and high-risk varices were 0.84 and 0.78, respectively. The summary specificities of PSR for any varices and high-risk varices were 0.78 and 0.67, respectively. The AUSROC of PSR for any varices at the threshold of 909 was 0.8867. The AUSROC of PSR for any varices in viral liver cirrhosis was 0.8675. The overall quality of studies was moderate. Significant heterogeneity and publication bias existed in the study. In conclusion, PSR can be used to identify varices in liver cirrhosis. PSR had a high sensitivity in viral liver cirrhosis.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Measurement of spleen stiffness to evaluate portal hypertension and the presence of esophageal varices in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Platelet count/spleen diameter ratio: proposal and validation of a non-invasive parameter to predict the presence of oesophageal varices in patients with liver cirrhosis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found