- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sphingosine-1-phosphate links glycosphingolipid metabolism to neurodegeneration via a calpain-mediated mechanism
Read this article at
Abstract
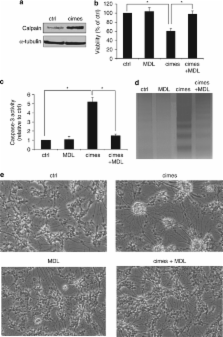
We have recently reported that the bioactive lipid sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), usually signaling proliferation and anti-apoptosis induces neuronal death when generated by sphingosine-kinase2 and when accumulation due to S1P-lyase deficiency occurs. In the present study, we identify the signaling cascade involved in the neurotoxic effect of sphingoid-base phosphates. We demonstrate that the calcium-dependent cysteine protease calpain mediates neurotoxicity by induction of the endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific caspase cascade and activation of cyclin-dependent kinase5 (CDK5). The latter is involved in an abortive reactivation of the cell cycle and also enhances tau phosphorylation. Neuroanatomical studies in the cerebellum document for the first time that indeed neurons with abundant S1P-lyase expression are those, which degenerate first in S1P-lyase-deficient mice. We therefore propose that an impaired metabolism of glycosphingolipids, which are prevalent in the central nervous system, might be linked via S1P, their common catabolic intermediate, to neuronal death.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found