- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
From bench to bed: the tumor immune microenvironment and current immunotherapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma
Read this article at
Abstract
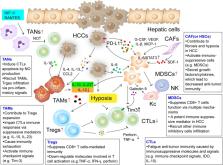
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks the most common primary liver malignancy and the third leading cause of tumor-related mortality worldwide. Unfortunately, despite advances in HCC treatment, less than 40% of HCC patients are eligible for potentially curative therapies. Recently, cancer immunotherapy has emerged as one of the most promising approaches for cancer treatment. It has been proven therapeutically effective in many types of solid tumors, such as non-small cell lung cancer and melanoma. As an inflammation-associated tumor, it’s well-evidenced that the immunosuppressive microenvironment of HCC can promote immune tolerance and evasion by various mechanisms. Triggering more vigorous HCC-specific immune response represents a novel strategy for its management. Pre-clinical and clinical investigations have revealed that various immunotherapies might extend current options for needed HCC treatment. In this review, we provide the recent progress on HCC immunology from both basic and clinical perspectives, and discuss potential advances and challenges of immunotherapy in HCC.
Related collections
Most cited references126
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Tumour hypoxia promotes tolerance and angiogenesis via CCL28 and T(reg) cells.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found