- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
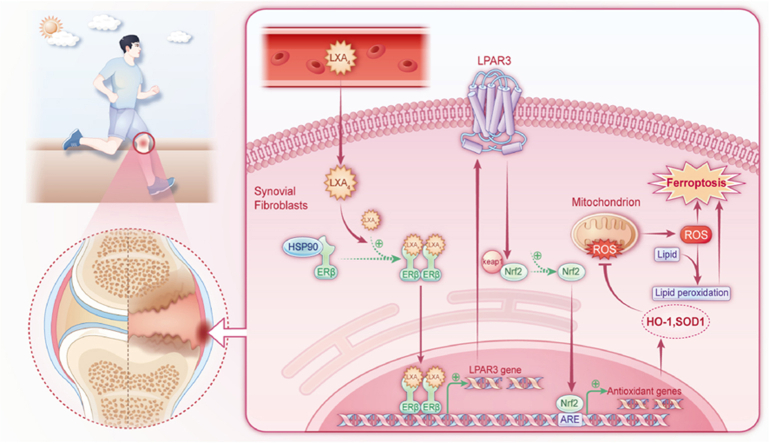
Lipoxin A 4 ameliorates knee osteoarthritis progression in rats by antagonizing ferroptosis through activation of the ESR2/LPAR3/Nrf2 axis in synovial fibroblast-like synoviocytes
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Our previous studies have shown that lipoxin A 4 (LXA 4) can serve as a potential biomarker for assessing the efficacy of exercise therapy in knee osteoarthritis (KOA), and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) may play a crucial role in KOA pain as well as in the progression of the pathology.
Objective
By analyzing the GSE29746 dataset and collecting synovial samples from patients with different Kellgren–Lawrence (KL) grades for validation, we focused on exploring the potential effect of LXA 4 on ferroptosis in FLSs through the ESR2/LPAR3/Nrf2 axis to alleviate pain and pathological advancement in KOA.
Methods
The association between FLSs ferroptosis and chondrocyte matrix degradation was explored by cell co-culture. We overexpressed and knocked down LPAR3 in vitro to explore its potential mechanism in FLSs. A rat model of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced KOA was constructed and intervened with moderate-intensity treadmill exercise and intraperitoneal injection of PHTPP to investigate the effects of the LXA 4 intracellular receptor ESR2 on exercise therapy.
Results
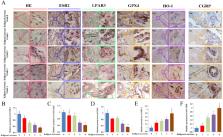
ESR2, LPAR3, and GPX4 levels in the synovium decreased with increasing KL grade. After LXA 4 intervention in the co-culture system, GPX4, LPAR3, and ESR2 were upregulated in FLSs, collagen II was upregulated in chondrocytes, and MMP3 and ADAM9 were downregulated. LPAR3 overexpression upregulated the expression of GPX4, Nrf2, and SOD1 in FLSs, while downregulating the expression of MMP13 and MMP3; LPAR3 knockdown reversed these changes. Moderate-intensity platform training improved the behavioral manifestations of pain in KOA rats, whereas PHTPP treatment partially reversed the improvement in synovial and cartilage pathologies induced by platform training.
Conclusion
LXA 4 inhibited FLSs ferroptosis by activating the ESR2/LPAR3/Nrf2 axis, thereby alleviating the pain and pathological progression of KOA. This study brings a new target for the treatment of KOA and also leads to a deeper understanding of the potential mechanisms of exercise therapy for KOA.
Graphical abstract
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found