- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
An electrophysiological signal that precisely tracks the emergence of error awareness
Read this article at
Abstract
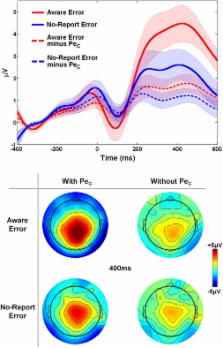
Recent electrophysiological research has sought to elucidate the neural mechanisms necessary for the conscious awareness of action errors. Much of this work has focused on the error positivity (Pe), a neural signal that is specifically elicited by errors that have been consciously perceived. While awareness appears to be an essential prerequisite for eliciting the Pe, the precise functional role of this component has not been identified. Twenty-nine participants performed a novel variant of the Go/No-go Error Awareness Task (EAT) in which awareness of commission errors was indicated via a separate speeded manual response. Independent component analysis (ICA) was used to isolate the Pe from other stimulus- and response-evoked signals. Single-trial analysis revealed that Pe peak latency was highly correlated with the latency at which awareness was indicated. Furthermore, the Pe was more closely related to the timing of awareness than it was to the initial erroneous response. This finding was confirmed in a separate study which derived IC weights from a control condition in which no indication of awareness was required, thus ruling out motor confounds. A receiver-operating-characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed that the Pe could reliably predict whether an error would be consciously perceived up to 400 ms before the average awareness response. Finally, Pe latency and amplitude were found to be significantly correlated with overall error awareness levels between subjects. Our data show for the first time that the temporal dynamics of the Pe trace the emergence of error awareness. These findings have important implications for interpreting the results of clinical EEG studies of error processing.
Related collections
Most cited references60
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The role of the medial frontal cortex in cognitive control.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The neural basis of human error processing: reinforcement learning, dopamine, and the error-related negativity.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found