- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Different metazoan parasites, different transcriptomic responses, with new insights on parasitic castration by digenetic trematodes in the schistosome vector snail Biomphalaria glabrata
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Gastropods of the genus Biomphalaria (Family Planorbidae) are exploited as vectors by Schistosoma mansoni, the most common causative agent of human intestinal schistosomiasis. Using improved genomic resources, overviews of how Biomphalaria responds to S. mansoni and other metazoan parasites can provide unique insights into the reproductive, immune, and other systems of invertebrate hosts, and their responses to parasite challenges.
Results
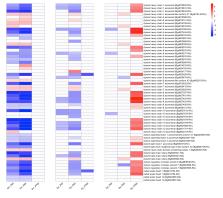
Using Illumina-based RNA-Seq, we compared the responses of iM line B. glabrata at 2, 8, and 40 days post-infection (dpi) to single infections with S. mansoni, Echinostoma paraensei (both digenetic trematodes) or Daubaylia potomaca (a nematode parasite of planorbid snails). Responses were compared to unexposed time-matched control snails. We observed: (1) each parasite provoked a distinctive response with a predominance of down-regulated snail genes at all time points following exposure to either trematode, and of up-regulated genes at 8 and especially 40dpi following nematode exposure; (2) At 2 and 8dpi with either trematode, several snail genes associated with gametogenesis (particularly spermatogenesis) were down-regulated. Regarding the phenomenon of trematode-mediated parasitic castration in molluscs, we define for the first time a complement of host genes that are targeted, as early as 2dpi when trematode larvae are still small; (3) Differential gene expression of snails with trematode infection at 40dpi, when snails were shedding cercariae, was unexpectedly modest and revealed down-regulation of genes involved in the production of egg mass proteins and peptide processing; and (4) surprisingly, D. potomaca provoked up-regulation at 40dpi of many of the reproduction-related snail genes noted to be down-regulated at 2 and 8dpi following trematode infection. Happening at a time when B. glabrata began to succumb to D. potomaca, we hypothesize this response represents an unexpected form of fecundity compensation. We also document expression patterns for other Biomphalaria gene families, including fibrinogen domain-containing proteins (FReDs), C-type lectins, G-protein coupled receptors, biomphalysins, and protease and protease inhibitors.
Related collections
Most cited references82

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found