- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
CD3 +CD4 -CD8 - (Double-Negative) T Cells in Inflammation, Immune Disorders and Cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
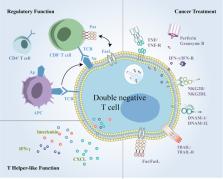
The crucial role of CD4 + and CD8 + T cells in shaping and controlling immune responses during immune disease and cancer development has been well established and used to achieve marked clinical benefits. CD3 +CD4 -CD8 - double-negative (DN) T cells, although constituting a rare subset of peripheral T cells, are gaining interest for their roles in inflammation, immune disease and cancer. Herein, we comprehensively review the origin, distribution and functions of this unique T cell subgroup. First, we focused on characterizing multifunctional DN T cells in various immune responses. DN regulatory T cells have the capacity to prevent graft-versus-host disease and have therapeutic value for autoimmune disease. T helper-like DN T cells protect against or promote inflammation and virus infection depending on the specific settings and promote certain autoimmune disease. Notably, we clarified the role of DN tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and outlined the potential for malignant proliferation of DN T cells. Finally, we reviewed the recent advances in the applications of DN T cell-based therapy for cancer. In conclusion, a better understanding of the heterogeneity and functions of DN T cells may help to develop DN T cells as a potential therapeutic tool for inflammation, immune disorders and cancer.
Related collections
Most cited references114
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Venetoclax combined with decitabine or azacitidine in treatment-naive, elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Six-of-the-best: unique contributions of γδ T cells to immunology.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found