- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Association between academic pressure, NR3C1 gene methylation, and anxiety symptoms among Chinese adolescents: a nested case-control study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Academic pressure is a prevalent stressor among Chinese adolescents and is often linked to anxiety symptoms, although the underlying mechanism remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the association between NR3C1 gene methylation, academic pressure, and anxiety symptoms among Chinese adolescents.
Methods
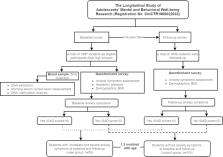
This nested-case control study included 150 adolescents (boys: 38.7%; baseline age: 12–17 years) from a school-based longitudinal study of Chinese adolescents. Cases (n = 50) were defined as those with anxiety symptoms at both baseline and follow-up, while controls (n = 100) were randomly selected from those without anxiety symptoms at both timepoints. The cases and controls were 1:2 matched by age. Academic pressure, anxiety symptoms, and potential covariates were measured using a self-report questionnaire. Peripheral whole blood samples were collected from each participant for the detection of cortisol level (i.e., morning serum cortisol level) and DNA methylation. The methylation analysis included a total of 27 CpG units at the NR3C1 promoter region.
Results
The final adjusted models showed that students with heavy academic pressure at baseline were at a higher risk of anxiety symptoms at follow-up compared to those with mild academic pressure ( β estimate: 6.24 [95% CI: 3.48 ~ 9.01]). After adjusting for covariates, the methylation level of one CpG unit ( NR3C1-16 CpG10) in NR3C1 differed significantly between cases and controls (F = 6.188, P = 0.014), and the difference remained significant after correction for multiple testing ( P < 0.025). The adjusted regression models showed that moderate ( β estimate = 0.010 [95% CI: 0.000 ~ 0.020], P = 0.046) and heavy ( β estimate = 0.011 [95% CI: 0.001 ~ 0.020], P = 0.030) academic pressure were significantly associated with the methylation level of NR3C1-16 CpG 10. Further mediation analysis demonstrated that the association of academic pressure and anxiety symptoms was significantly mediated by the methylation of NR3C1-16 CpG 10 ( β estimate for indirect effect = 0.11 [95% CI: 0.005 ~ 0.32]; indirect/total effect = 8.3%).
Conclusion
The present study suggests that NR3C1-16 CpG 10 DNA methylation might be a potential mechanism that partially explains the lasting effects of academic pressure on subsequent anxiety symptoms among adolescents. Further studies with larger sample sizes are recommended to replicate this finding.
Related collections
Most cited references54
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
DNA methylation and its basic function.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found