- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
NETosis in Alzheimer’s Disease
Read this article at
Abstract
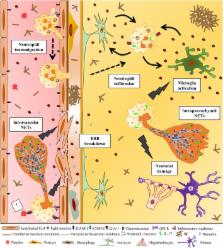
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive deterioration of cognitive functions. Its neuropathological features include amyloid-β (Aβ) accumulation, the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, and the loss of neurons and synapses. Neuroinflammation is a well-established feature of AD pathogenesis, and a better understanding of its mechanisms could facilitate the development of new therapeutic approaches. Recent studies in transgenic mouse models of AD have shown that neutrophils adhere to blood vessels and migrate inside the parenchyma. Moreover, studies in human AD subjects have also shown that neutrophils adhere and spread inside brain vessels and invade the parenchyma, suggesting these cells play a role in AD pathogenesis. Indeed, neutrophil depletion and the therapeutic inhibition of neutrophil trafficking, achieved by blocking LFA-1 integrin in AD mouse models, significantly reduced memory loss and the neuropathological features of AD. We observed that neutrophils release neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) inside blood vessels and in the parenchyma of AD mice, potentially harming the blood–brain barrier and neural cells. Furthermore, confocal microscopy confirmed the presence of NETs inside the cortical vessels and parenchyma of subjects with AD, providing more evidence that neutrophils and NETs play a role in AD-related tissue destruction. The discovery of NETs inside the AD brain suggests that these formations may exacerbate neuro-inflammatory processes, promoting vascular and parenchymal damage during AD. The inhibition of NET formation has achieved therapeutic benefits in several models of chronic inflammatory diseases, including autoimmune diseases affecting the brain. Therefore, the targeting of NETs may delay AD pathogenesis and offer a novel approach for the treatment of this increasingly prevalent disease.
Related collections
Most cited references96
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Platelet TLR4 activates neutrophil extracellular traps to ensnare bacteria in septic blood.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found