- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Antifertility activity of Cryptolepis sanguinolenta leaf ethanolic extract in male rats
Read this article at
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Complementary medicine has grown over time with more botanicals emerging and remaining integral parts of medicare. Such botanicals include Cryptolepis sanguinolenta.
AIM:
This study investigated the effect of Cryptolepis sanguinolenta leaf ethanolic extract on male reproductive system using rat model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Control and treated rats were maintained on control diet. Treated rats also received graded doses of the extract.
RESULTS:
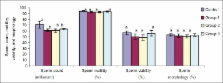
When compared with the controls, Cryptolepis sanguinolenta treatment led to significant testosterone suppression associated with consequent significant rise in luteinizing hormone (LH) and decrease in sperm count. Treatment with Cryptolepis sanguinolenta did not result in significant attenuation of follicular stimulating hormone (FSH) levels and testicular morphometry. Sperm viability, motility, and morphology were also comparable in all groups.
Related collections
Most cited references72
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
In vitro and in vivo antiplasmodial activity of cryptolepine and related alkaloids from Cryptolepis sanguinolenta.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The DNA intercalating alkaloid cryptolepine interferes with topoisomerase II and inhibits primarily DNA synthesis in B16 melanoma cells.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Plants used in home medicine in the Zenta River basin, Northwest Argentina.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.