- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Epidural dexmedetomidine or esketamine versus fentanyl to decrease ropivacaine use for labor analgesia: A randomized non-inferiority study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Epidural nonopioid adjuvants also reduce local anesthetic use. We aimed to test the hypothesis that, compared with the present standard fentanyl, the hourly consumption of local anesthetic was at least as good when dexmedetomidine or esketamine was combined with local anesthetic for patient-controlled epidural analgesia (PCEA).
Methods
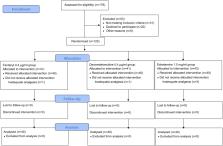
A total of 120 laboring nulliparous subjects requiring labor analgesia were recruited for the final statistical analysis. Subjects were randomized to receive 0.075 % ropivacaine added with one of three equivalent adjuvants: 0.4 μg/mL fentanyl, 0.4 μg/mL dexmedetomidine, or 1.0 mg/mL esketamine. The primary outcome was hourly ropivacaine consumption. Compared with the fentanyl group, a 20 % difference in hourly local anesthetic consumption between the dexmedetomidine and esketamine groups was considered a clinical difference (non-inferiority margin).
Results
The hourly ropivacaine consumption of the fentanyl group was 12.4 (95 % confidence interval CI 11.2 to 13.6) ml/h, so the prespecified non-inferiority limit was 2.5 ml/h. The hourly ropivacaine consumption of the fentanyl group was not inferior to that of the dexmedetomidine group (12.4 ml/h vs. 11.9 ml/h, risk difference, 0.5; 95 % confidence interval CI, −1.0 to 2.0, meeting criteria for non-inferiority). However, the hourly ropivacaine consumption of the esketamine group was 14.3 ml/h, and that of the fentanyl group was 12.4 ml/h (risk difference, 1.9, 95 % CI, 0.2 to 3.6), failing to confirm non-inferiority with a non-inferiority margin of 20 %. The incidence of pruritus was highest in the fentanyl group, whereas the occurrence of mild dizziness was highest in the esketamine group.
Conclusions
In setting of the conditions of this study, epidural dexmedetomidine was non-inferior compared with epidural fentanyl in combination with ropivacaine for PCEA during labor. Meanwhile, we failed to establish the non-inferiority of epidural esketamine compared with epidural fentanyl in combination with ropivacaine for labor analgesia.
Highlights
-
•
Epidural nonopioid adjuvants also reduce local anesthetic use.
-
•
No trial has been performed to show the non-inferiority of the hourly consumption of local anaesthetics using these equivalent adjuncts in combination with local anaesthetics for PCEA.
-
•
Epidural dexmedetomidine was non-inferior compared with epidural fentanyl in combination with ropivacaine for PCEA during labor.
-
•
We failed to establish the non-inferiority of epidural esketamine compared with epidural fentanyl in combination with ropivacaine for labor analgesia.
Related collections
Most cited references28
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Dural Puncture Epidural Technique Improves Labor Analgesia Quality With Fewer Side Effects Compared With Epidural and Combined Spinal Epidural Techniques: A Randomized Clinical Trial.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparison of dexmedetomidine and sufentanil as adjuvants to local anesthetic for epidural labor analgesia: a randomized controlled trial
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found