- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Genome-wide Association of Hypoxia-inducible Factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α DNA Binding with Expression Profiling of Hypoxia-inducible Transcripts*
Read this article at
Abstract
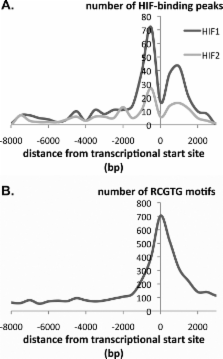
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) controls an extensive range of adaptive responses to hypoxia. To better understand this transcriptional cascade we performed genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation using antibodies to two major HIF-α subunits, and correlated the results with genome-wide transcript profiling. Within a tiled promoter array we identified 546 and 143 sequences that bound, respectively, to HIF-1α or HIF-2α at high stringency. Analysis of these sequences confirmed an identical core binding motif for HIF-1α and HIF-2α (RCGTG) but demonstrated that binding to this motif was highly selective, with binding enriched at distinct regions both upstream and downstream of the transcriptional start. Comparison of HIF-promoter binding data with bidirectional HIF-dependent changes in transcript expression indicated that whereas a substantial proportion of positive responses (>20% across all significantly regulated genes) are direct, HIF-dependent gene suppression is almost entirely indirect. Comparison of HIF-1α- versus HIF-2α-binding sites revealed that whereas some loci bound HIF-1α in isolation, many bound both isoforms with similar affinity. Despite high-affinity binding to multiple promoters, HIF-2α contributed to few, if any, of the transcriptional responses to acute hypoxia at these loci. Given emerging evidence for biologically distinct functions of HIF-1α versus HIF-2α understanding the mechanisms restricting HIF-2α activity will be of interest.
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found