- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
High expression of the putative cancer stem cell marker, DCLK1, in rectal neuroendocrine tumors
Read this article at
Abstract
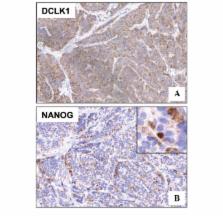
Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1), a microtubule-associated protein, is known to regulate neuronal differentiation, migration and neurogenesis. Recent evidence suggests that the protein is a putative marker for intestinal and pancreatic stem cells, including their cancer stem cell counterparts. The present study conducted immunohistochemical analyses for DCLK1 and the stemness marker, NANOG, in human intestinal neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), as their expression had not been previously investigated in these tumors. Eighteen patients with endoscopically resected rectal NETs were enrolled in the study. The mean age of the patients was 51 years old. The mean diameter of the resected tumors was 5.2 mm, and a histological diagnosis of NET grade G1 was formed for all tumors. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed not only for DCLK1, but also for the known NET markers, synaptophysin, chromogranin A and cluster of differentiation (CD)56. The intensity and distribution of staining were scored on a scale of 0–3 and 0–2, respectively. The sum of the scores was calculated for each specimen. Co-expression of DCLK1 and NANOG was also examined. The mean scores for DCLK1 and synaptophysin were significantly higher than those for chromogranin A (P<0.0001) and CD56 (P<0.01). There were no significant differences in the scores between DCLK1 and synaptophysin or between chromogranin A and CD56. Notably, NANOG was expressed in high quantities in all the tumor tissues studied, showing clear co-expression with DCLK1. In conclusion, DCLK1 may be a novel marker for rectal NET, potentially indicating the presence of the stemness gene product, NANOG.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Dclk1 distinguishes between tumor and normal stem cells in the intestine.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Long-lived intestinal tuft cells serve as colon cancer-initiating cells.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found