- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy vs placebo in a predominantly Chinese population with type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 11): a double-blind, Phase IIIa, randomised trial

Read this article at
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis
The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy vs placebo in a predominantly Chinese population with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled with diet and exercise alone.
Methods
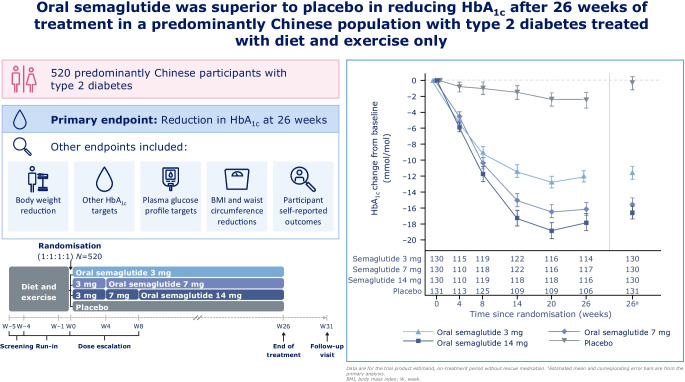
The Peptide Innovation for Early Diabetes Treatment (PIONEER) 11 trial was a double-blind, randomised, Phase IIIa trial conducted across 52 sites in the China region (mainland China and Taiwan), Hungary, Serbia and Ukraine. Eligible participants were ≥18 years (≥20 years in Taiwan), had a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes with HbA 1c 53–86 mmol/mol (7.0–10.0%) and were not receiving any glucose-lowering drugs. After a 4-week run-in period in which participants were treated with diet and exercise alone, those who fulfilled the randomisation criteria were randomised (1:1:1:1) using a web-based randomisation system to receive once-daily oral semaglutide 3 mg, 7 mg or 14 mg or placebo for 26 weeks (using a 4-week dose-escalation regimen for the higher doses). Randomisation was stratified according to whether participants were from the China region or elsewhere. The primary and confirmatory secondary endpoints were change from baseline to week 26 in HbA 1c and body weight (kg), respectively. Safety was assessed in all participants exposed to at least one dose of the trial product.
Results
Between October 2019 and October 2021, a total of 774 participants were screened and 521 participants were randomised to oral semaglutide 3 mg ( n=130), 7 mg ( n=130), 14 mg ( n=130) or placebo ( n=131); most participants (92.5%, n=482) completed the trial, with 39 participants prematurely discontinuing treatment. The number of participants contributing to the trial analyses was based on the total number of participants who were randomised at the beginning of the trial. The majority of participants were male (63.7%), and the mean age of participants was 52 years. At baseline, mean HbA 1c and body weight were 63 mmol/mol (8.0%) and 79.6 kg, respectively. Oral semaglutide resulted in significantly greater reductions in HbA 1c than placebo at week 26 ( p<0.001 for all doses). The estimated treatment differences (ETDs [95% CIs]) for oral semaglutide 3 mg, 7 mg and 14 mg vs placebo were –11 (–13, –9) mmol/mol, –16 (–18, –13) mmol/mol and –17 (–19, –15) mmol/mol, respectively. The corresponding ETDs in percentage points (95% CI) vs placebo were –1.0 (–1.2, –0.8), –1.4 (–1.6, –1.2) and –1.5 (–1.8, –1.3), respectively. Significantly greater reductions in body weight were also observed for oral semaglutide 7 mg and 14 mg than for placebo at week 26 (ETD [95% CI] –1.2 kg [–2.0 kg, –0.4 kg; p<0.01] and –2.0 kg [–2.8 kg, –1.2 kg; p<0.001], respectively), but not for oral semaglutide 3 mg (ETD [95% CI] –0.0 kg [–0.9 kg, 0.8 kg; not significant]). Similar reductions in HbA 1c and body weight were observed in the Chinese subpopulation, which represented 74.9% of participants in the overall population. Adverse events (AEs) occurred in between 65.4% and 72.3% of participants receiving oral semaglutide (for all doses) and 57.3% of participants with placebo. Most AEs were mild to moderate in severity, with few serious AEs reported; the most commonly reported AEs were gastrointestinal-related and were more frequent with semaglutide (all doses) than with placebo. The proportion of AEs was slightly higher in the Chinese subpopulation.
Conclusions/interpretation
Oral semaglutide resulted in significantly greater reductions in HbA 1c across all doses and in significant body weight reductions for the 7 mg and 14 mg doses when compared with placebo in predominantly Chinese participants with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled by diet and exercise alone. Oral semaglutide was generally well tolerated, with a safety profile consistent with that seen in the global PIONEER trials.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found