- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Geothermal and structural features of La Palma island (Canary Islands) imaged by ambient noise tomography
Read this article at
Abstract
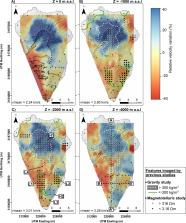
La Palma island is located in the NW of the Canary Islands and is one of the most volcanically active of the archipelago, therefore the existence of geothermal resources on the island is highly probable. The main objective of this work is to detect velocity anomalies potentially related to active geothermal reservoirs on La Palma island, by achieving a high-resolution seismic velocity model of the first few kilometres of the crust using Ambient Noise Tomography (ANT). The obtained ANT model is merged with a recent local earthquake tomography model. Our findings reveal two high-velocity zones in the island’s northern and southern parts, that could be related to a plutonic intrusion and old oceanic crust materials. Conversely, four low-velocity zones are imaged in the southern part of the island. Two of them can be related to hydrothermal alteration zones located beneath the Cumbre Vieja volcanic complex. This hypothesis is reinforced by comparing the S-wave velocity model with the seismicity recorded during the pre-eruptive phase of the 2021 Tajogaite eruption, which revealed an aseismic volume coinciding with these low-velocity zones. Another low-velocity zone is observed in the southern part of the island, which we interpret as highly fractured rocks which could favour the ascent of hot fluids. A last low-velocity zone is observed in the central part of the island and associated with loose deposits generated by the Aridane valley mega landslide.
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
High-Resolution Surface-Wave Tomography from Ambient Seismic Noise
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found