- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Complications of miliary tuberculosis: low mortality and predictive biomarkers from a UK cohort
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Untreated, miliary tuberculosis (TB) has a mortality approaching 100%. As it is uncommon there is little specific data to guide its management. We report detailed data from a UK cohort of patients with miliary tuberculosis and the associations and predictive ability of admission blood tests with clinical outcomes.
Methods
Routinely collected demographic, clinical, blood, imaging, histopathological and microbiological data were assessed for all patients with miliary TB identified from the London TB register from 2008 to 2012 from Northwest London Hospitals NHS Trust. Multivariable logistic regression was used to assess factors independently associated with the need for critical care intervention. Receiver operator characteristics (ROC) were calculated to assess the discriminatory ability of admission blood tests to predict clinical outcomes.
Results
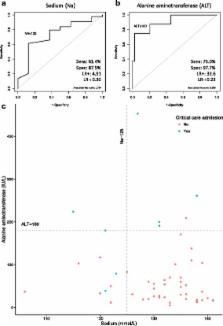
Fifty-two patients were identified with miliary tuberculosis, of whom 29% had confirmed central nervous system (CNS) involvement. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was more sensitive than computed tomography (CT) or lumbar puncture for detecting CNS disease. Severe complications were frequent, with 15% requiring critical care intervention with mechanical ventilation. This was independently associated with admission hyponatraemia and elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Having an admission sodium ≥125 mmol/L and an ALT <180 IU/L had 82% sensitivity and 100% specificity for predicting a favourable outcome with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.91. Despite the frequency of severe complications, one-year mortality was low at 2%.
Related collections
Most cited references9
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global mortality, disability, and the contribution of risk factors: Global Burden of Disease Study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Miliary tuberculosis: new insights into an old disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found