- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Age-specific sex difference in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma possesses a notable sex difference in incidence, and a protective role of estrogens has been hypothesized.
Methods
Using data from 13 cancer registries in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, we describe the age-specific sex difference in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States during 1992-2013. We used a curve fitting by non-linear regression to quantitatively characterize the age-specific incidence rate of hepatocellular carcinoma by sex.
Results
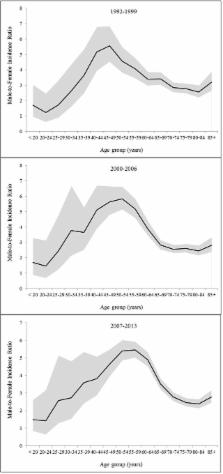
A total of 44,287 incident cases of hepatocellular carcinoma (33,196 males and 11,091 females) were included, with an overall male-to-female ratio in age-standardized rate of 3.55. The sex ratio was below 2 at ages <25 years, increased with age from ages 25-29 years until peaking at 5.40 at ages 50-54 years, and declined thereafter. We also observed additional peaks in the age-specific sex ratio curves at ages 25-34 years across racial/ethnic groups. Modelling of age-specific incidence rates indicated a 15-year delayed increase with age in females compared with males in Asian and Pacific Islanders, and an 11-year delay in Hispanic whites.
Conclusions
The age-dependent patterns in the sex difference in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma support the hypothesis of a protective role of estrogens. The underlying reasons for the sex difference in hepatocellular carcinoma remain to be further explored in analytic epidemiological studies.
Related collections
Most cited references16
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Gender Disparity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Roles of Sex Hormones
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Lifetime risk and sex difference of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic hepatitis B and C.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found