- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Infodemic and fake news – A comprehensive overview of its global magnitude during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021: A scoping review
Read this article at
Abstract
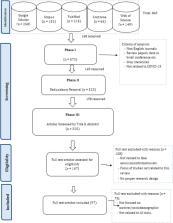
The spread of fake news increased dramatically during the COVID-19 pandemic worldwide. This study aims to synthesize the extant literature to understand the magnitude of this phenomenon in the wake of the pandemic in 2021, focusing on the motives and sociodemographic profiles, Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based tools developed, and the top trending topics related to fake news. A scoping review was adopted targeting articles published in five academic databases (January 2021–November 2021), resulting in 97 papers. Most of the studies were empirical in nature (N = 69) targeting the general population (N = 26) and social media users (N = 13), followed by AI-based detection tools (N = 27). Top motives for fake news sharing include low awareness, knowledge, and health/media literacy, Entertainment/Pass Time/Socialization, Altruism, and low trust in government/news media, whilst the phenomenon was more prominent among those with low education, males and younger. Machine and deep learning emerged to be the widely explored techniques in detecting fake news, whereas top topics were related to vaccine, virus, cures/remedies, treatment, and prevention. Immediate intervention and prevention efforts are needed to curb this anti-social behavior considering the world is still struggling to contain the spread of the COVID-19 virus.
Related collections
Most cited references88
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
