- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Geriatric syndromes and subsequent health-care utilization among older community dwellers in Stockholm
Read this article at
Abstract
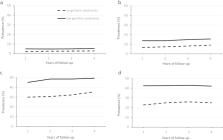
Little is known about the long-term effect of geriatric syndromes on health-care utilization. This study aims to determine the association between geriatric syndromes and health-care utilization during a four-year period among older community dwellers. Based on the Stockholm Public Health Cohort study, a total number of 6700 community dwellers aged ≥65 years were included. From a baseline survey in 2006, geriatric syndromes were defined as having at least one of the following: insomnia, functional decline, urinary incontinence, depressive symptoms and vision impairment. Health-care utilization was identified by linkages at individual level with register data with a four-year follow-up. Cox regression was performed to estimate the associations. Compared to those without geriatric syndromes, participants with any geriatric syndromes had a higher prevalence of frequent hospitalizations, long hospital stays, frequent outpatient visits and polypharmacy in each of the follow-up years. After controlling for covariates, having any geriatric syndromes was associated with higher levels of utilization of inpatient and outpatient care as well as polypharmacy. The association was stable over time, and the fully adjusted hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) remained stable in frequent hospitalizations (from 1.89 [1.31, 2.73] in year 1 to 1.70 [1.23, 2.35] in year 4), long hospital stay (from 1.75 [1.41, 2.16] to 1.49 [1.24, 1.78]), frequent outpatient visits (from 1.40 [1.26, 1.54] to 1.33 [1.22, 1.46]) and polypharmacy (from 1.63 [1.46, 1.83] to 1.53 [1.37, 1.71]). Having any geriatric syndromes is associated with higher levels of health-care utilization among older community dwellers, and the impact of geriatric syndromes is stable over a four-year period.
Related collections
Most cited references24
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Aging with multimorbidity: a systematic review of the literature.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Ageing populations: the challenges ahead.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found