- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Open Schools, Covid-19, and Child and Teacher Morbidity in Sweden
letter
Jonas F. Ludvigsson , M.D., Ph.D.
Lars Engerström , M.D., Ph.D.
Charlotta Nordenhäll , M.D., Ph.D.
Emma Larsson , M.D., Ph.D.
06 January 2021
Keyword part (code): 4Keyword part (keyword): PediatricsKeyword part (code): 4_1Keyword part (keyword): Pediatrics General ,
4,
Pediatrics,
Keyword part (code): 4_1Keyword part (keyword): Pediatrics General,
4_1,
Pediatrics General,
Keyword part (code): 10Keyword part (keyword): Emergency MedicineKeyword part (code): 10_1Keyword part (keyword): Emergency Medicine General ,
10,
Emergency Medicine,
Keyword part (code): 10_1Keyword part (keyword): Emergency Medicine General,
10_1,
Emergency Medicine General,
Keyword part (code): 12Keyword part (keyword): Pulmonary/Critical CareKeyword part (code): 12_1Keyword part (keyword): Pulmonary/Critical Care General ,
12,
Pulmonary/Critical Care,
Keyword part (code): 12_1Keyword part (keyword): Pulmonary/Critical Care General,
12_1,
Pulmonary/Critical Care General,
Keyword part (code): 18Keyword part (keyword): Infectious DiseaseKeyword part (code): 18_6Keyword part (keyword): Viral Infections ,
18,
Infectious Disease,
Keyword part (code): 18_6Keyword part (keyword): Viral Infections,
18_6,
Viral Infections
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Abstract
To the Editor: In mid-March 2020, many countries decided to close schools in an attempt
to limit the spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2),
the virus causing coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19).
1,2
Sweden was one of the few countries that decided to keep preschools (generally caring
for children 1 to 6 years of age) and schools (with children 7 to 16 years of age)
open. Here, we present data from Sweden on Covid-19 among children 1 to 16 years of
age and their teachers. In Sweden, Covid-19 was prevalent in the community during
the spring of 2020.
3
Social distancing was encouraged in Sweden, but wearing face masks was not.
3
Data on severe Covid-19, as defined by intensive care unit (ICU) admission, were prospectively
recorded in the nationwide Swedish intensive care registry. We followed all children
who were admitted to an ICU between March 1 and June 30, 2020 (school ended around
June 10) with laboratory-verified or clinically verified Covid-19, including patients
who were admitted for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C, which
is likely to be related to Covid-19)
4
according to the Swedish Pediatric Rheumatology Quality Register. (More information
on the registry and a link to the Word Health Organization scientific brief on MIS-C
are provided in the Supplementary Appendix, available with the full text of this letter
at NEJM.org.) The Stockholm Ethics Review Board approved the study. Informed consent
was waived by the review board.
The number of deaths from any cause among the 1,951,905 children in Sweden (as of
December 31, 2019) who were 1 to 16 years of age was 65 during the pre–Covid-19 period
of November 2019 through February 2020 and 69 during 4 months of exposure to Covid-19
(March through June 2020) (see the Supplementary Appendix). From March through June
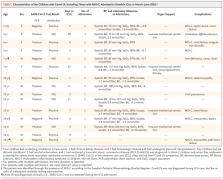
2020, a total of 15 children with Covid-19 (including those with MIS-C) were admitted
to an ICU (0.77 per 100,000 children in this age group) (Table 1), 4 of whom were
1 to 6 years of age (0.54 per 100,000) and 11 of whom were 7 to 16 years of age (0.90
per 100,000). Four of the children had an underlying chronic coexisting condition
(cancer in 2, chronic kidney disease in 1, and hematologic disease in 1). No child
with Covid-19 died.
Data from the Public Health Agency of Sweden (published report
5
and personal communication) showed that fewer than 10 preschool teachers and 20 schoolteachers
in Sweden received intensive care for Covid-19 up until June 30, 2020 (20 per 103,596
schoolteachers, which is equal to 19 per 100,000). As compared with other occupations
(excluding health care workers), this corresponded to sex- and age-adjusted relative
risks of 1.10 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.49 to 2.49) among preschool teachers
and 0.43 (95% CI, 0.28 to 0.68) among schoolteachers (see the Supplementary Appendix).
The present study had some limitations. We lacked data on household transmission of
Covid-19 from schoolchildren, and the 95% confidence intervals for our results are
wide.
Despite Sweden’s having kept schools and preschools open, we found a low incidence
of severe Covid-19 among schoolchildren and children of preschool age during the SARS-CoV-2
pandemic. Among the 1.95 million children who were 1 to 16 years of age, 15 children
had Covid-19, MIS-C, or both conditions and were admitted to an ICU, which is equal
to 1 child in 130,000.
Related collections
Most cited references4
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019
Na Zhu, Dingyu Zhang, Wenling Wang … (2020)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical Characteristics of 58 Children With a Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated With SARS-CoV-2
Elizabeth Whittaker, Alasdair Bamford, Julia Kenny … (2020)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
School closure and management practices during coronavirus outbreaks including COVID-19: a rapid systematic review
Russell M Viner, Simon J Russell, Helen Croker … (2020)
