- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Integrated analysis identifies TfR1 as a prognostic biomarker which correlates with immune infiltration in breast cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
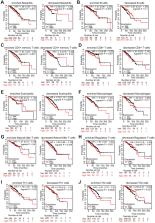
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common malignancy with high morbidity and mortality in females worldwide. Emerging evidence indicates that transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) plays vital roles in regulating cellular iron import. However, the distinct role of TfR1 in BC remains elusive. TfR1 expression was investigated using the TCGA, GEO, TIMER, UALCAN and Oncomine databases. The prognostic potential of TfR1 was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier (KM) plotter and univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. Moreover, Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) were used to explore the molecular mechanism of TfR1. The potential link between TfR1 expression and infiltrating abundances of immune cells was examined through the TIMER and CIBERSORT algorithm. The expression of TfR1 was dramatically upregulated in BC tissues. Increased TfR1 expression and decreased methylation levels of TfR1 were strongly correlated with multiple clinicopathological parameters. Elevated TfR1 expression was associated with a poor survival rate in BC patients. The nomogram model further confirmed that TfR1 could act as an independent prognostic biomarker in BC. The results of GO, KEGG and GSEA revealed that TfR1 was closely correlated with multiple signaling pathways and immune responses. Additionally, TfR1 was positively associated with the infiltration abundances of six major immune cells, including CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, B cells, neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells in BC. Interestingly, TfR1 influenced prognosis partially through immune infiltration. These comprehensive bioinformatics analyses suggest that TfR1 is a new independent prognostic biomarker and a potential target for immunotherapy in BC.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Iron and cancer: more ore to be mined.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found