- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/Akt pathway
Read this article at
Abstract
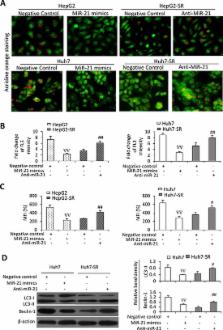
Sorafenib resistance remains a major obstacle for the effective treatments of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent studies indicate that activated Akt contributes to the acquired resistance to sorafenib, and miR-21 dysregulates phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), which inhibits Akt activation. Sorafenib-resistant HCC cells were shown to be refractory to sorafenib-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. Akt and its downstream factors were highly activated and/or upregulated in sorafenib-resistant cells. Inhibition of autophagy decreased the sensitivity of sorafenib-resistant cells to sorafenib, while its induction had the opposite effect. Differential screening of miRNAs showed higher levels of miR-21 in sorafenib-resistant HCC cells. Exposure of HCC cells to sorafenib led to an increase in miR-21 expression, a decrease in PTEN expression and sequential Akt activation. Transfection of miR-21 mimics in HCC cells restored sorafenib resistance by inhibiting autophagy. Anti-miR-21 oligonucleotides re-sensitized sorafenib-resistant cells by promoting autophagy. Inhibition of miR-21 enhances the efficacy of sorafenib in treating sorafenib-resistant HCC tumors in vivo. We conclude that miR-21 participates in the acquired resistance of sorafenib by suppresing autophagy through the Akt/PTEN pathway. MiR-21 could serve as a therapeutic target for overcoming sorafenib resistance in the treatment of HCC.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Beclin 1-VPS34 complex--at the crossroads of autophagy and beyond.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found