- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Evaluating the Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Officially Recommended in China for COVID-19 Using Ontology-Based Side-Effect Prediction Framework (OSPF) and Deep Learning
Read this article at
Abstract
Ethnopharmacological relevance
The novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak in Wuhan has imposed a huge influence in terms of public health and economy on society. However, no effective drugs or vaccines have been developed so far. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has been considered as a promising supplementary treatment of this disease due to its clinically proven performance in many severe diseases, like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Meanwhile, many reports suggest that the side-effects (SE) of TCM prescriptions cannot be ignored in treating COVID-19 as it often leads to dramatic degradation of the patients’ physical condition. Systematic evaluation of TCM regarding its latent SE becomes a burning issue.
Aim
In this study, we used an ontology-based side-effect prediction framework (OSPF) developed from our previous work and Artificial Neural Network (ANN)-based deep learning, to evaluate the TCM prescriptions officially recommended by China for the treatment of COVID-19.
Materials and methods
The OSPF developed from our previous work was implemented in this study, where an ontology-based model separated all ingredients in a TCM prescription into two categories: hot and cold. A database was created by converting each TCM prescription into a vector which contained ingredient dosages, corresponding hot/cold attribution and safe/unsafe labels. This allowed for training of the ANN model. A safety indicator (SI), as a complement to SE possibility, was then assigned to each TCM prescription. According to the proposed SI, from high to low, the recommended prescription list could be optimized. Furthermore, in interest of expanding the potential treatment options, SIs of other well-known TCM prescriptions, which are not included in the recommended list but are used traditionally to cure flu-like diseases, are also evaluated via this method.
Results
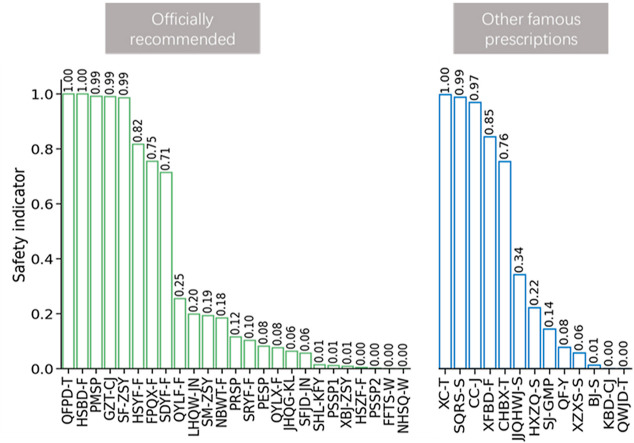
Based on SI, QFPD-T, HSBD-F, PMSP, GCT-CJ, SF-ZSY, and HSYF-F were the safest treatments in the recommended list, with SI scores over 0.8. PESP, QYLX-F, JHQG-KL, SFJD-JN, SHL-KFY, PESP1, XBJ-ZSY, HSZF-F, PSSP2, FFTS-W, and NHSQ-W were the prescriptions most likely to be unsafe, with SI scores below 0.1. In the additional lists of other TCM prescriptions, the indicators of XC-T, SQRS-S, CC-J, and XFBD-F were all above 0.8, while QF-Y, XZXS-S, BJ-S, KBD-CJ, and QWJD-T’s indicators were all below 0.1.
Conclusions
In total, there were 10 TCM prescriptions with indicators over 0.8, suggesting that they could be considered in treating COVID-19, if suitable. We believe this work could provide reasonable suggestions for choosing proper TCM prescriptions as a supplementary treatment for COVID-19. Furthermore, this work introduces a novel and informative method which could help create recommendation list of TCM prescriptions for the treatment of other diseases.
Graphical abstract
Related collections
Most cited references18
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Deep learning.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Individual Comparisons by Ranking Methods
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found