- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cell Type-Selective Expression of Circular RNAs in Human Pancreatic Islets
Read this article at
Abstract
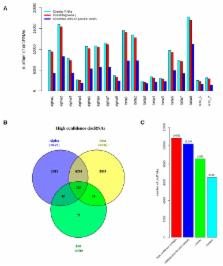
Understanding distinct cell-type specific gene expression in human pancreatic islets is important for developing islet regeneration strategies and therapies to improve β-cell function in type 1 diabetes (T1D). While numerous transcriptome-wide studies on human islet cell-types have focused on protein-coding genes, the non-coding repertoire, such as long non-coding RNA, including circular RNAs, remains mostly unexplored. Here, we explored transcriptional landscape of human α-, β-, and exocrine cells from published total RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) datasets to identify circular RNAs (circRNAs). Our analysis revealed that circRNAs are highly abundant in both α- and β-cells. We identified 10,830 high-confidence circRNAs expressed in human α-, β-, and exocrine cells. The most highly expressed candidates were MAN1A2, RMST, and HIPK3 across the three cell-types. Alternate circular isoforms were observed for circRNAs in the three cell-types, indicative of potential distinct functions. Highly selective α- and β-cell circRNAs were identified, which is suggestive of their potential role in regulating β-cell function.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Genome-wide analysis of drosophila circular RNAs reveals their structural and sequence properties and age-dependent neural accumulation.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Diverse alternative back-splicing and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found